Ligustrum, Nǚ Zhēn Zi, 女貞子, Fructus Ligustri Lucidi
Disclaimer For educational purposes only. Do not use as medical advice
Ligustrum Vulgare Privet - the leaves of Common Privet Ligustrum japonicum - Japanese Privet Ligustrum ovalifolium - California Privet Ligustrum sinense - Chinese Privet USA: Ligustrum lucidum has been Introduced to multiple states USDA Zones: 8-10. Native: China Habitats: River valleys, roadsides, elevation<2900m Herbal medicine may interact negatively with pharma drugs and other herbs. Examples below: Herbs: ♦ Antidiabetic: Mei Gui Hua, Du Zhong, Dang Shen, HuoLong Guo, rougui, Celery, Chamomile, Moringa Tree, Basil, Ku Gua, Hibiscus, Gou Qi Zi, Ju Hua, Xia Ku Cao, Dang Gui, Zhi Mu, Shi gao, Xuan Shen, Cang Zhu, Shan yao, Huang Qi, Artichoke, Gan Cao Pharma Drugs:♦ Antidiabetic: Acarbose (Precose ) , Albiglutide (Tanzeum) , Alogliptin (Nesina) , Bromocriptine mesylate (Cycloset , Canaglifozin (Invokana) , Chlorpropamide (Diabinese) , Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) , Dulaglutide (Trulicity) , Empagliflozin (Jardiance) , Glimepiride (Amaryl) , glipizide (Glucotrol) , Glyburide (DiaBeta , Glynase) , Insulin , Linagliptin (Tradjenta) , Metformin , Miglitol (Glyset) , Nateglinide (Starlix) , Parlodel) , Pioglitazone (Actos) , Pramlintide , Repaglinide (Prandin) , Rosiglitazone (Avandia) , Saxagliptin (Onglyza) , Sitagliptin (Januvia) , Tol-Tab) , Tolazamide (Tolinase) , Tolbutamide (Orinase)
Health Benefits
For: Menopause • Hot flashes • Cold feet • Night sweats • Tidal fever • Irritability • Mood swings • Dry eyes • Constipation • Irritated eyes • Blur vision • Macular degeneration • Diabetes • Cholesterol • Hepatitis • Premature gray hair • Acute lower back pain
Attributes: Anti-aging • Antibiotic • Anticholesterol • Antidiabetic • Anti-inflammatory • Immunity booster • Hepatoprotective
Products (online examples)



Photos (Click to enlarge)
Fun Facts
Other Names: Glossy privet fruit • 女贞子 • Dong Qing Zi • Nu Zhen Shi • Nu Zhen • Joteishi (Japanese)
Plant Family: Oleaceae
Species
Growth
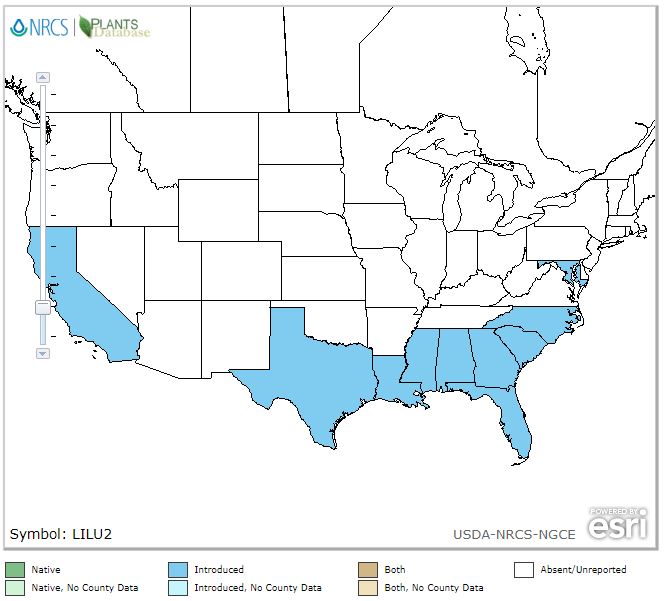
Ligustrum lucidum is in the USDA Plant Database. Drill down via USDA Interactive Map:
Category: Tonify Yin
English: Ligustrum Pinyin: Nu Zhen Zi Pharmaceutical: Fructus Ligustri Lucidi
Organs: Kidney • Liver Temperature: Cool
Taste: Sweet • Bitter Toxicity: None noted
Patterns: Kidney yin deficiency • Kidney jing deficiency • Liver yin deficiency • Liver jing deficiency • Menopause
Actions: Tonify liver and kidney yin • Tonify liver and kidney essence • Clear heat • Moisten eyes • Treat menopausal symptoms
Indications: Dry eyes • Irritated eyes • Blur vision • Hot flashes • Cold feet • Night sweats • Tidal fever • Irritability • Menopause • Mood swings • Tinnitus
Contraindications: Yang deficiency • Spleen cold • Stomach cold • Diarrhea • Pregnancy • Children under 12 • Asthma • Olive pollen allergies
Typical Dosage: 10g to 15g Guidelines
Parts Used: Seed • Bark • Leaves
Other: Nu Zhen Zi tea can be made by steeping 2 tablespoons of dry herb in a cup of water for 35 to 45 minutes.
Combine With
Purpose
Sha Yuan Zi
Liver and kidney deficiency: dizziness, blurred vision, ringing in ear[5]
Ju Hua + Shen Di Huang + Gou Qi Zi + Sha Yuan Zi
Kidney Yin deficiency - blurred vision, poor memory, ringing in ear[17]
Di Gu Pi + Mu Dan Pi
Clear yin deficient heat[5]
Xia Ku Cao + Di Gu Pi + Qing Hao
Tuberculosis with intermittent high fever[5]
Qing Xiang Zi + Jue Ming Zi
Wind heat, painful blood-shot eyes[5]
Gou Qi Zi + Shu Di Huang
Liver and kidney deficiency with blurry vision[5]
Gou Qi Zi + Shu Di Huang + Tu Si Zi + Fu Pen Zi + Chu Shi Zi
Liver and kidney deficiency with blurry vision[18]
Han Lian Cao + Yin Chai Hu + He Huan Hua + Long Gu + Mu Li
Irritability and mood swings from menopause [18]
Di Gu Pi + Qing Hao + Bai Wei + Hu Huang Lian
Hot flashes; Steaming Bone disorder [18]
Di Gui Pi + Shen Di Huang + Mu Dan Pi
Steaming bone disorder, fever, seminal discharge and night sweats [17]
Fu Xiao Mai + Wu Wei Zi
Menopausal night sweat (severe hot flashes at night) [18]
Bu Gu Zhi + Tu Si Zi
Kidney in deficiency with lower back pain, dizziness, and fatigue [5]
Mai Men Dong + Sheng Di Huang
Excessive thirst [18]
Zhi He Shou Wu + Hei Zhi Ma
Premature hair graying[5]
Han Lian Cao + Sang Shen
Premature graying lower back pain and dizziness from liver and kidney yin deficiency[17]
Dui Yao Pairs
Purpose
Formulas with Nu Zhen Zi
Er Zhi Wan
Alert
Be cautions with all medicine.
Potential Drug Interactions
Information in this post came from many sources, including class notes, practitioners, websites, webinars, books, magazines, and editor's personal experience. While the original source often came from historical Chinese texts, variations may result from the numerous English translations. Always consult a doctor prior to using these drugs. The information here is strictly for educational purposes.










0 Comments