Artemisia Capillaris, Yīn Chén Hāo, 茵陈蒿, Herba Artemisiae Capillaris
Disclaimer For educational purposes only. Do not use as medical advice
Attributes: Antioxidant • Anticoagulant • Anti-inflammatory • Antiviral • Antifibrotic • Antitumor • Antidiabetic • Cholagogue • Choleretic • Diuretic • Hepatoprotective • Hypoglycemic • Hypotensive This herb is commonly used to treat jaundice. Externally, the herb is often used alone as a topical agent to relief sores, itchy skin and eczema. It clears damp liver heat and damp gallbladder heat. This herb is often used as an adulterant for Artemisia Annua, which is on the World Health Organization's list of antimalarial drugs. There are five popular species of artemisia, each with different medicinal uses. We've included multiple species in the product sample section. Be cautions to order the correct species. This blog is focused on Artemisia Capillaris. Artemisiae Scopariae (Mian Yin Chen) • 绵茵陈 - the Eurasian species similar to A. Capillaris. Artemisia Annua (Qing Hao) • 青蒿 • Sweet Sagewort - Antimalarial. On WHO's list of drugs against malaria. It's the source of artemisinin, the active ingredient in antimalarial pharmaceutical drugs. Artemisia Absinthium (Ai Hao) • 艾蒿- Digestive issues, liver disease, depression, worm infections, Crohn's disease, sexual stimulant, insecticide, hallucinogenic. It is used to make the alcoholic beverage call Absinthe. This beverage is banned in France, Switzerland and the United States. [ref], [ref2] Artemisia Argyi (Ai Ye) • 艾叶 - Stops bleeding. Nosebleed, excessive menstruation, bloody mucous, bloody vomit, bloody urine, bleeding gum. Used in moxibustion sticks. Artemisia Vulgaris (Bei Ai) • 北艾- Common wormwood. Insect repellent and intestinal worms. Often used as a substitute for Artemisia Argyi (Ai Ye). USA: Artemisia Capillaris is not found in the wild in the US. However, a substitute, Artemisiae Scopariae has been introduced into Maryland. Artemisia Annua, Artemisia Absinthium, and Artemisia Vulgaris are very different varieties of this plant and should not be used as substitutes. Some are poisonous. USDA Zones: 5 to 8 ( Artemisia Capillaris) World: China, Philippines, Korea, Japan, Manchuria Habitats: River banks, hills, roadsides, seashores, dried sandy fields Herbal medicine may interact negatively with pharma drugs and other herbs. Examples below: Herbs: ♦Anticoagulants: American Ginseng, Arnica, Rou Gui, Chamomile, Dan Shen, Dang Gui, Deertongue, Sheng Jiang, Goji Berry, Ginko Nutes, Notoginseng, Peach Kernel, Hong Hua, Sweet Clover, Vanilla Grass ♦ Antidiabetic: Mei Gui Hua, Du Zhong, Dang Shen, HuoLong Guo, rougui, Celery, Chamomile, Moringa Tree, Basil, Ku Gua, Hibiscus, Gou Qi Zi, Ju Hua, Xia Ku Cao, Dang Gui, Zhi Mu, Shi gao, Xuan Shen, Cang Zhu, Shan yao, Huang Qi, Artichoke, Gan Cao ♦ Diuretic: Heal All, Bai Zhu, Huang Qi, Da Fu Pi, Ma huang, Du Zhong ♦ Hypotensive: ginseng, goji berry, cinnamon Pharma Drugs:♦Anticoagulants: asprin , clopidogrel (Plavix) , Coumadin , dipyridamole , enoxaparin , Heparin ♦ High blood pressure: captopril (Capoten), benazepril (Lotensin), Perindopril (Aceon), irbesartan (Avapro), telmisartan (Micardis), valsartan (Diovan), acebutolol (Sectral), carvedilol (Coreg), metoprolol (Lopressor), amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine (Plendil), verapamil (Calan), labetalol (Trandate) ♦ Diuretic: Acetazolamide, Aldactone, Amiloride Hydrochloride, Bumex, Diuril, Diulo, Demadex, Dyrenium, Edecrin, Enduron, Hydrodiuril, Hygroton, Lasix, Lozol, Methazolamide, Mykrox, Zaroxolyn ♦ Antidiabetic: Acarbose (Precose ) , Albiglutide (Tanzeum) , Alogliptin (Nesina) , Bromocriptine mesylate (Cycloset , Canaglifozin (Invokana) , Chlorpropamide (Diabinese) , Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) , Dulaglutide (Trulicity) , Empagliflozin (Jardiance) , Glimepiride (Amaryl) , glipizide (Glucotrol) , Glyburide (DiaBeta , Glynase) , Insulin , Linagliptin (Tradjenta) , Metformin , Miglitol (Glyset) , Nateglinide (Starlix) , Parlodel) , Pioglitazone (Actos) , Pramlintide , Repaglinide (Prandin) , Rosiglitazone (Avandia) , Saxagliptin (Onglyza) , Sitagliptin (Januvia) , Tol-Tab) , Tolazamide (Tolinase) , Tolbutamide (Orinase)
Health Benefits
For: Jaundice • Diabetes • High blood pressure • Liver disease • Liver cirrhosis • Hepatitis • Fibrosis • Foot fungal infection (topical)
Products (online examples)


Photos (Click to enlarge)
Fun Facts
Other Names: A. scoparia • A. capillaris • Wormwood • Mian Yin Chen • Mian Chen
Plant Family: Asteraceae
Artemisia has over 300 species. Yin Chen Hao are the leaves and shoots of either Artemisia Capillaris or Artemisiae Scopariae. A Scopariae is often call Mian Yin Chen.
Species
Artemisia Capillaris (Yin Chen Hao)• 茵陈蒿 - Popularly used for jaundice. Good for liver diseases and gastric ulcers.
Growth
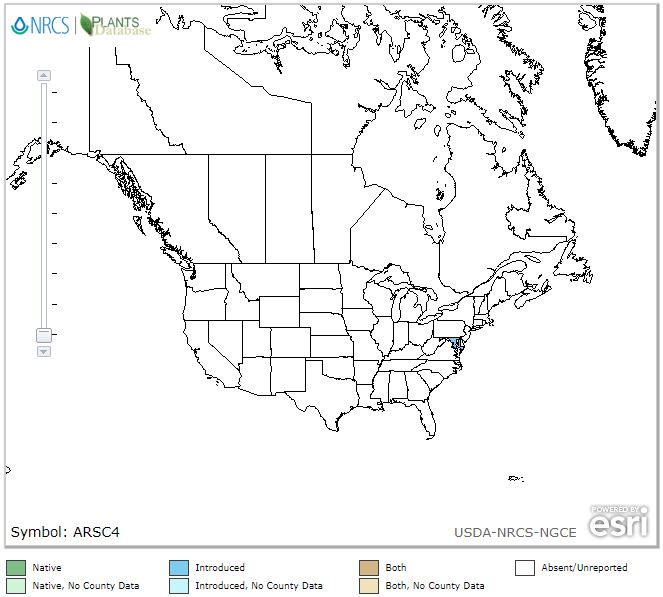
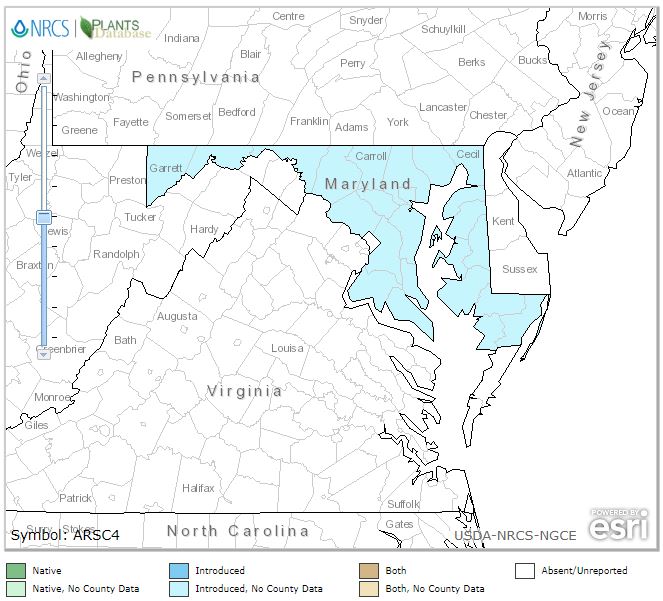
Artemisia Capillaris is not in the USDA database. A substitute, Artemisiae Scopariae can be found in the following locations. Drill down via USDA Interactive Map:
Properties, Actions, Indications, etc. Category: Drain Dampness
English: Artemisia Capillaris Pinyin: Yin Chen Pharmaceutical: Herba Artemisiae Capillaris
Organs: Gallbladder • Liver • Spleen • Stomach Temperature: Cool
Taste: Bitter • Pungent Toxicity: None noted
Patterns: Liver damp heat • Gallbladder damp heat
Actions: Clear liver damp heat • Clear gallbladder damp heat • Release exterior • Relieve jaundice
Indications: Intermittent fever • Chills • Poor appetite • Nausea • Dizziness
Contraindications: Blood deficiency • Vaginal discharge and spermatorrhea • Diuretic drugs • Blood pressure pills • Anticoagulant medication
Typical Dosage: 9g to 30g Guidelines
Parts Used: Shoots • Leaves
Other:
Combine With
Purpose
Zhi Zi + Huang Bai + Da Huang + Che Qian Zi
Treats yang jaundice and gallbladder heat [17]
Fu Zi + Gan Jiang + Bai Zhu + Ze Xie
Treats yin jaundice with damp cold [17]
Guang Huo + Bai Dou Kou + Tong Cao + Hou Po
Dampness with nausea, chest tightness, and mild fever [17]
Huang Bai + Di Fu Zi + Tu Fu Ling
Dampness with itch skin, sores, hives, and eczema [17]
Zhi Zi + Da Huang (Yin Chen Hao Tang)
Treats yang jaundice from damp heat in liver and gallbladder. [14] Hepatitis. Liver Cirrhosis.
Gan Jiang + Fu Zi + Fu Ling
Treats yin jaundice with damp cold [5]
Hou Po
Jaundice from summer heat dampness and middle burner obstruction [5]
Hua Shi
Jaundice from summer heat with difficult urination [5]
Fu Ling + Gui Zhi + Ze Xie
Jaundice from dampness with difficult urination [3]
Chai Hu + Jin Qian Cao + Da Huang + Yu Jin
Cholecystitis [3]
Huang Qin
Damp heat skin rashes [3]
Bai Hua She She Cao + Hu Zhang
Liver Cirrhosis [3]
Huang Qin + Jin Qian Cao + Bai Hua She She Cao + Chai Hu
Hepatitis [3]
Formulas with Yin Chen
Gan Lu Xiao Du Dan • Yin Chen Hao Tang • Zhen Gan Xi Feng Tang
Alert
Be cautions with all medicine.
Potential Drug Interactions
Information in this post came from many sources, including class notes, practitioners, websites, webinars, books, magazines, and editor's personal experience. While the original source often came from historical Chinese texts, variations may result from the numerous English translations. Always consult a doctor prior to using these drugs. The information here is strictly for educational purposes.








0 Comments